Hearing Test
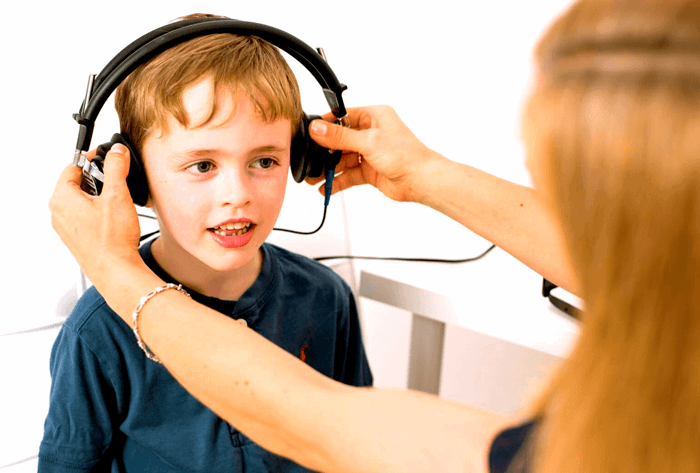

Pure Tone Audiometry
Pure-tone audiometry is a hearing test performed by an audiologist to measure the faintest sound intensity (threshold) a person can hear across a range of pitches (frequencies). This diagnostic tool helps determine the degree (how much hearing is lost), type (conductive, sensorineural, or mixed), and configuration (pattern) of hearing loss. The results are plotted on an audiogram, a graph showing hearing sensitivity, which guides diagnosis and management.
Purpose of the Test:
Measure hearing sensitivity: Identifies the softest pure tone a person can hear at specific frequencies.
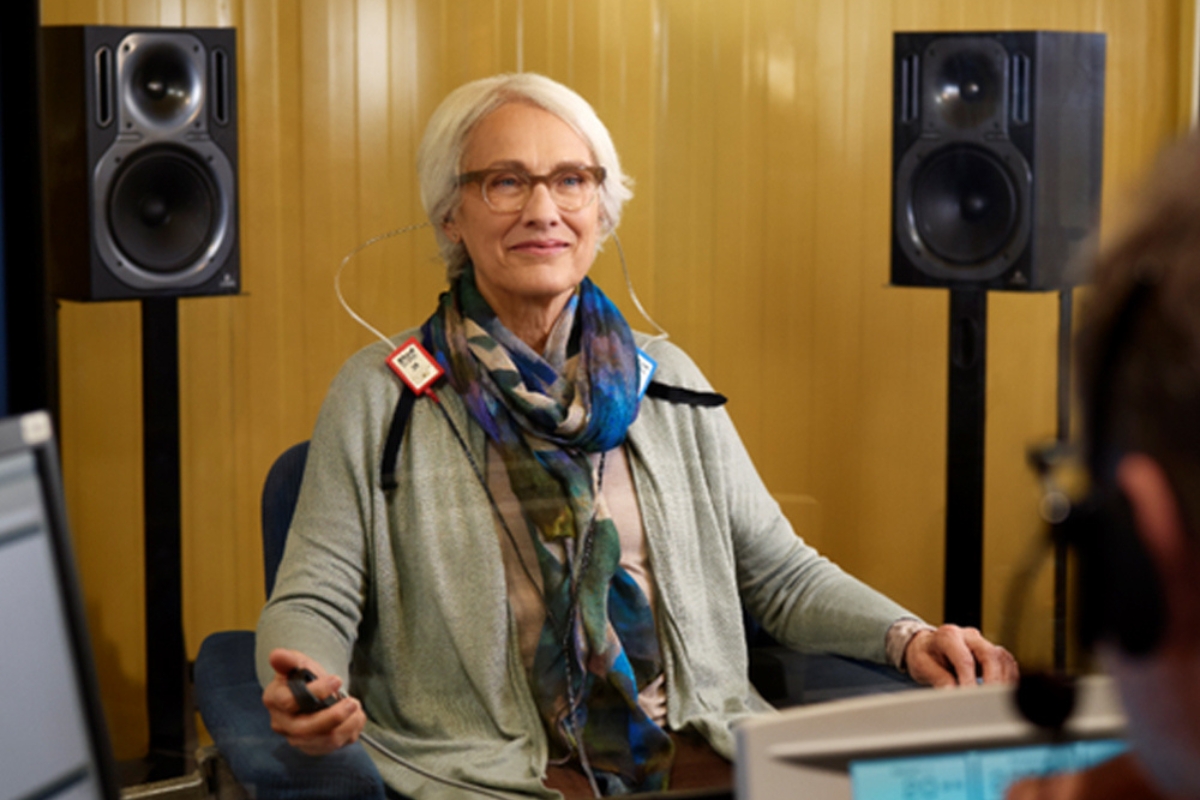

Free Field Audiometry
Free field audiometry, also known as sound-field audiometry, is a hearing test that uses speakers to present sounds to a person in a room, rather than using headphones. This method is useful for individuals, especially infants, toddlers, and those with special needs, who cannot tolerate headphones. The test can assess hearing sensitivity to pure tones and speech, check for hearing defects, and evaluate the effectiveness of hearing aids in a real-world sound environment.
How it works Speakers?
Sounds are delivered through one or more loudspeakers positioned around the patient.

Tinnitus matching
Tinnitus matching is a psychoacoustic test where an audiologist presents external sounds to a patient and asks them to match the pitch and loudness of their tinnitus to the external sound, typically using an audiometer. The goal is to characterize the perceived tinnitus, especially its pitch and loudness, for use in sound-based therapies like tinnitus masking. Despite challenges, such as the subjective nature of tinnitus and potential co-existing hearing loss, tinnitus matching is a valuable assessment to help individuals understand their tinnitus and to guide treatment.
How Tinnitus Matching Works?
To determine the perceived frequency (pitch) and intensity (loudness) of the tinnitus.

Hearing Aids (Invisible)
Invisible hearing aids, such as Invisible-in-Canal (IIC) devices, are custom-made, discreet hearing solutions that fit deep inside the ear canal, becoming virtually unnoticeable to others. They are ideal for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss who want to maintain a natural look and feel confident while improving their hearing. While they offer benefits like natural sound quality and reduced wind noise, their small size can make battery handling difficult, and they typically lack features found in larger devices, such as Bluetooth connectivity and user-accessible controls.
How they work:
IIC hearing aids are custom-molded to fit the wearer's unique ear canal, ensuring comfort and a secure fit.
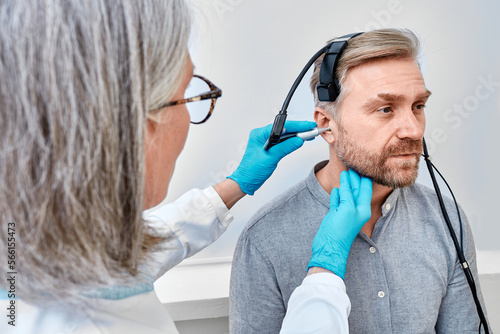
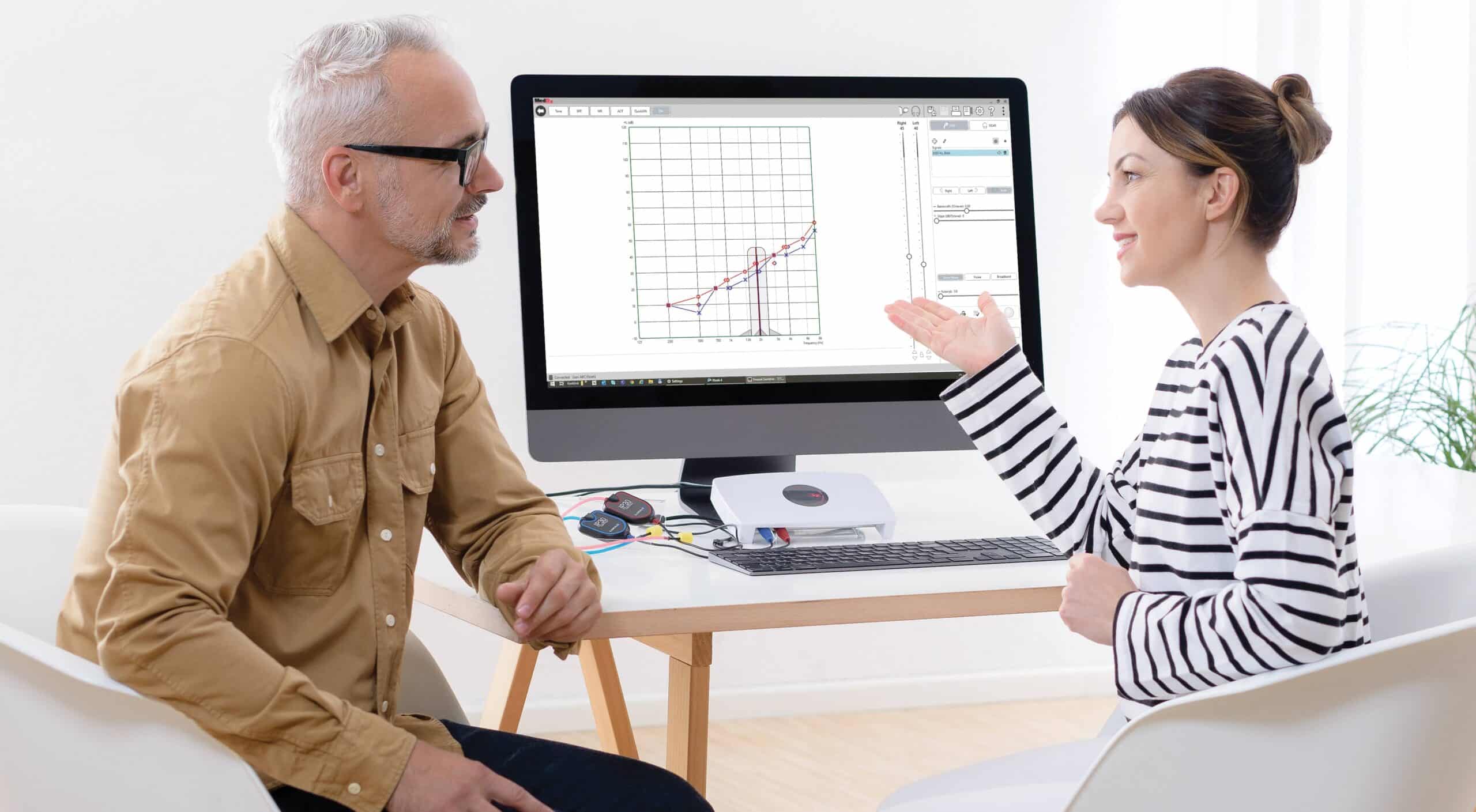
Impedance
Impedance Test for the Ear or Impedance Audiometry Is a painless non-invesive test that means-ures the pressure and movement of the eardrum and middle ear Identifying condition like fluid buildup eardrum damge or, Eustachian tube problem.
Combination of Resistance and Reactance:
Resistance (R): The basic opposition to current flow, similar to friction, and is present in all circuits, including DC.
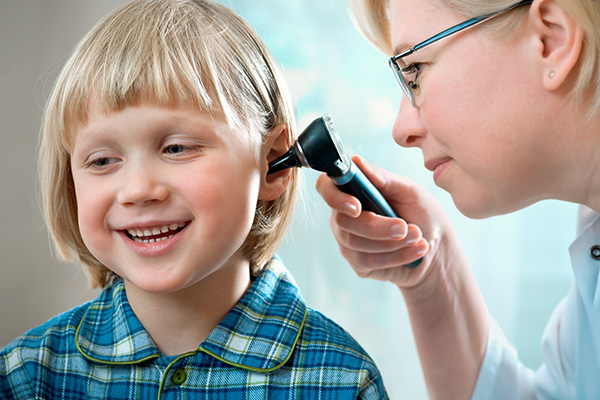

Hearing Aid Trail & Fitting
A hearing aid trial and fitting involves an audiologist selecting and programming hearing aids for you to try for a period, then making adjustments to ensure they are comfortable, effective, and customized to your specific hearing loss through a process of tests and fine-tuning. During the fitting, you receive instructions on use and maintenance, understand the trial period and warranty, and can ask questions before beginning the adaptation period to new sounds.
What is a hearing aid trial and fitting?
You test different hearing aids for a set period to find the best fit for your hearing loss and lifestyle.
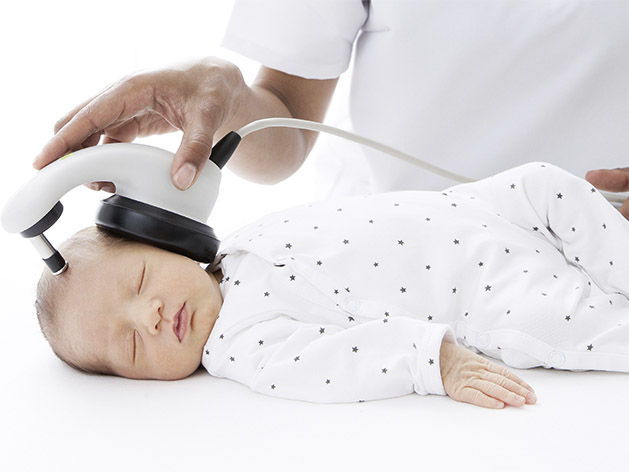

Bera Assr
"Bera Assr" refers to a combined or integrated system for conducting both Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA) and Auditory Steady-State Response (ASSR) tests, which are electrophysiological hearing assessment methods used to evaluate the auditory system. BERA (also known as ABR) assesses electrical activity in the auditory nerve and brainstem, while ASSR measures steady-state responses to determine hearing thresholds, particularly for assessing different frequencies
BERA (Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry):
Measures the brain's electrical response to sound at the level of the auditory nerve and brainstem
Helps diagnose retrocochlear issues and evaluate hearing thresholds
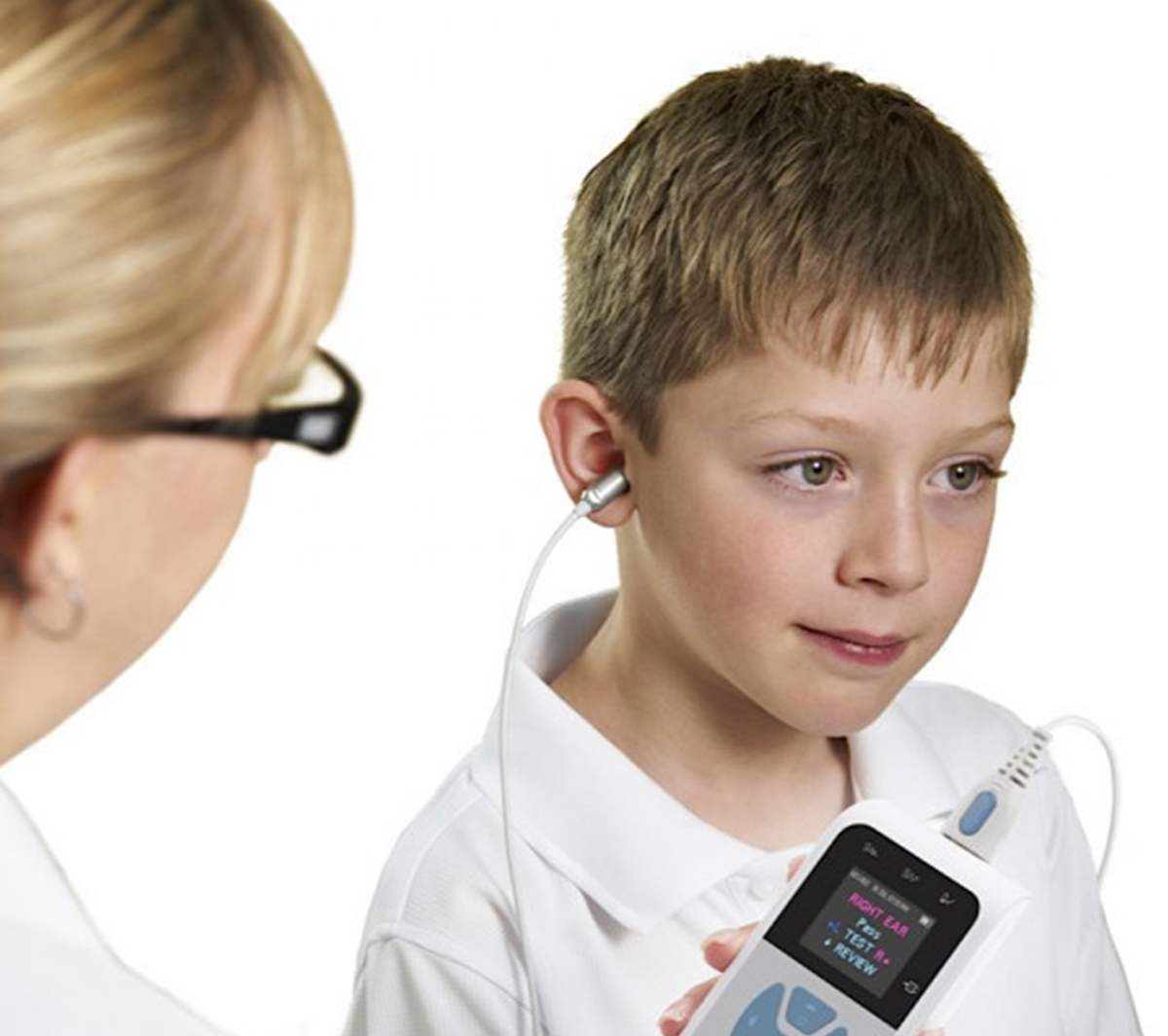
OAE
OAE stands for Otoacoustic Emission. It refers to sounds produced by the inner ear, or cochlea, in response to an external stimulus, a process that indicates healthy function of the hair cells in the inner ear. An Otoacoustic Emission test is a painless, objective hearing test that uses a small probe to send sounds into the ear canal and record the emissions. The results are used to screen for hearing loss in infants, children, and adults, as they provide a quick and reliable way to assess the health of the cochlea.
How OAE Testing Works
Stimulus Delivery: A small probe is placed in the ear canal, emitting soft sounds or clicks.
Not being able to swallow.