Speech Therapy
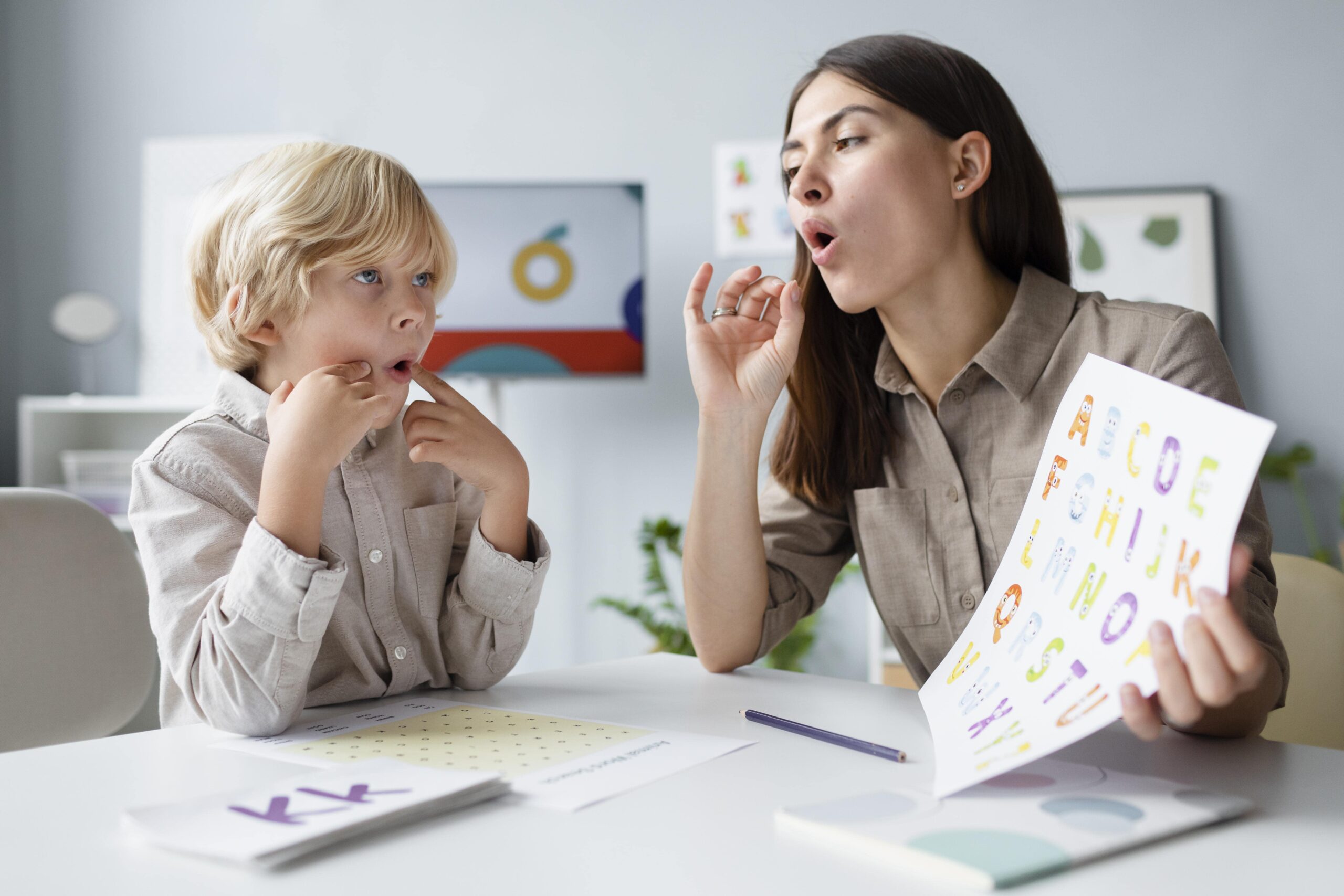

Misarticulation
Misarticulation is a speech disorder involving the incorrect or distorted production of speech sounds, where individuals may substitute, omit, distort, or add sounds in words. It is not a physical defect but can stem from factors like structural issues (e.g., a cleft palate), hearing loss, developmental delays, or persistent incorrect speech habits. Common errors include saying "wabbit" for "rabbit" or "thun" for "sun"
Misarticulation can be caused by several factors:
Structural differences: Issues with the tongue, jaw, lips, or palate, or the frenulum (tissue under the tongue).
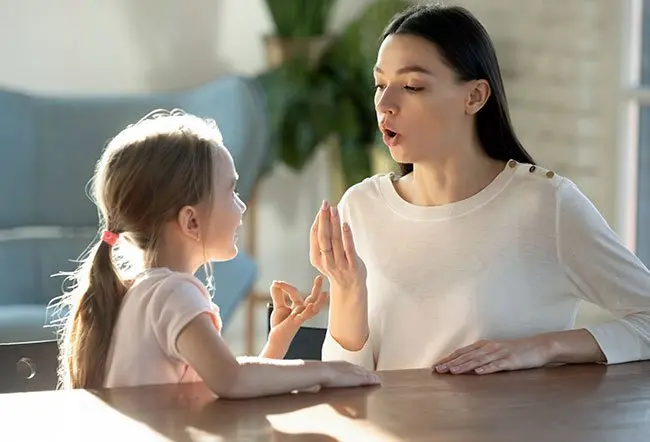

Stuttering
Stuttering, or stammering, is a speech disorder where the flow of speech is interrupted by repetitions, prolongations, and pauses, known as "blocks". It is common in young children and often resolves on its own, but can persist into adulthood and requires treatment from a speech-language pathologist. Treatment focuses on techniques to improve fluency and communication, with early intervention recommended for preschool-aged children to maximize recovery.
What is it?
Disrupted Speech Flow: Stuttering disrupts the natural rhythm and flow of speech.

Aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder, not a loss of intelligence, caused by brain damage that affects the ability to communicate through speaking, reading, writing, and understanding language. It is commonly caused by a stroke, head injury, or brain tumor, and can also be a symptom of progressive neurological diseases like Alzheimer's. Symptoms vary widely but can include trouble finding words, forming sentences, or comprehending language, and the condition is treated with therapy to relearn skills and find new communication methods.
What Causes Aphasia?
Aphasia results from damage to the brain's language centers, typically in the left hemisphere.
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from damage to the nervous system, leading to weak or poorly controlled speech muscles, which affects the clarity, speed, strength, or coordination of speech. It can cause slurred, mumbled, slow, or difficult-to-understand speech. Common causes include stroke, head injuries, and neurological conditions like Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, or cerebral palsy. Speech therapy is often used to help manage the condition and improve communication.
Slurred or mumbled speech:
Speech may be hard to understand.

Carebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a permanent group of movement and posture disorders caused by damage to the developing brain, most often before, during, or after birth, which affects the brain's ability to control muscles and coordinate movement. Symptoms can include stiff muscles (spasticity), poor coordination, weak muscles, tremors, and problems with balance and posture.Cerebral palsy can also affect other functions like speech, vision, hearing, and eating.
Problems with brain development:
In some cases, the areas of the brain that control movement don't develop as expected in the womb.

Autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder, is a condition characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a need or strong preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing differences, focused interests, and repetitive behaviors. Characteristics of autism are present from early childhood and the condition typically persists throughout life. Clinically classified as a neurodevelopmental disorder.
Social and communication skills
Autistic people may have differences in social communication and interaction, which can lead to challenges in environments structured around neurotypical norms.

Hearing Impaired
Impaired hearing, or hearing loss, is a partial or complete inability to hear sounds, resulting from damage or disease in the ear or auditory nerves, or from blockages like earwax. It can manifest as difficulty hearing conversations, especially in noisy environments, or needing to ask people to repeat themselves. Treatment varies by cause and severity and may include removing earwax, using hearing aids, or getting a cochlear implant.
Types of Hearing Loss:
Conductive Hearing Loss: Caused by issues in the outer or middle ear, preventing sound from being conducted effectively to the inner ear.
Mixed Hearing Loss: Involves both conductive and sensorineural components.
Swallowing Disorder
Dysphagia is a medical term for difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia can be a painful condition. In some cases, swallowing is impossible. Occasional difficulty swallowing, such as when you eat too fast or don't chew your food well enough, usually isn't cause for concern.Dysphagia is a medical term for difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia can be a painful condition. In some cases, swallowing is impossible.
Symptoms associated with dysphagia can include:
Pain while swallowing.
Not being able to swallow.

Voice disorders
A voice disorder is a condition that alters your vocal quality, pitch, or loudness, causing persistent changes like hoarseness, breathiness, strain, or voice fatigue. Causes vary from growths on the vocal cords, to nerve damage, vocal misuse, neurological conditions like spasmodic dysphonia, and even psychological issues. Treatment depends on the cause, and can include voice therapy, medication, or surgery.
Common Symptoms:
Hoarseness: A rough, breathy, or weak-sounding voice.
Voice Fatigue: Your voice tires easily

Mental Retardation
"Mental retardation" is an outdated and stigmatizing term for intellectual disability, a condition characterized by significantly below-average intellectual functioning and limitations in adaptive behaviors, such as communication, self-care, and social skills. It is a developmental disorder that manifests before the age of 18 and can result from genetic factors, problems during pregnancy, birth complications, or acquired brain damage. Diagnosis involves both intelligence quotient (IQ) testing and an assessment of adaptive skills needed for daily living
Below-average intellectual functioning:
Often indicated by an IQ score below 70-75:

Delayed Speech & Language
A speech and language delay occurs when a child does not meet typical communication milestones for their age. Speech delay affects the ability to produce sounds, while a language delay impacts the understanding or use of words and sentences. Causes can range from hearing loss and developmental disorders to psychosocial factors like limited adult interaction. Diagnosis involves a doctor's assessment and referral to a speech-language pathologist (SLP) for testing.
Speech Delay:
This refers to the difficulty in producing sounds to form words and sentences. A child with a speech delay may use age-appropriate language but struggle to be understood